What are Batteries?

Batteries are electrochemical devices that store chemical energy and convert it into electrical energy. They are essentially portable power sources that enable us to power various devices, from everyday items like smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage systems.
How Batteries Work, What is battery
Batteries function by harnessing the movement of electrons through a chemical reaction. The basic components of a battery include:
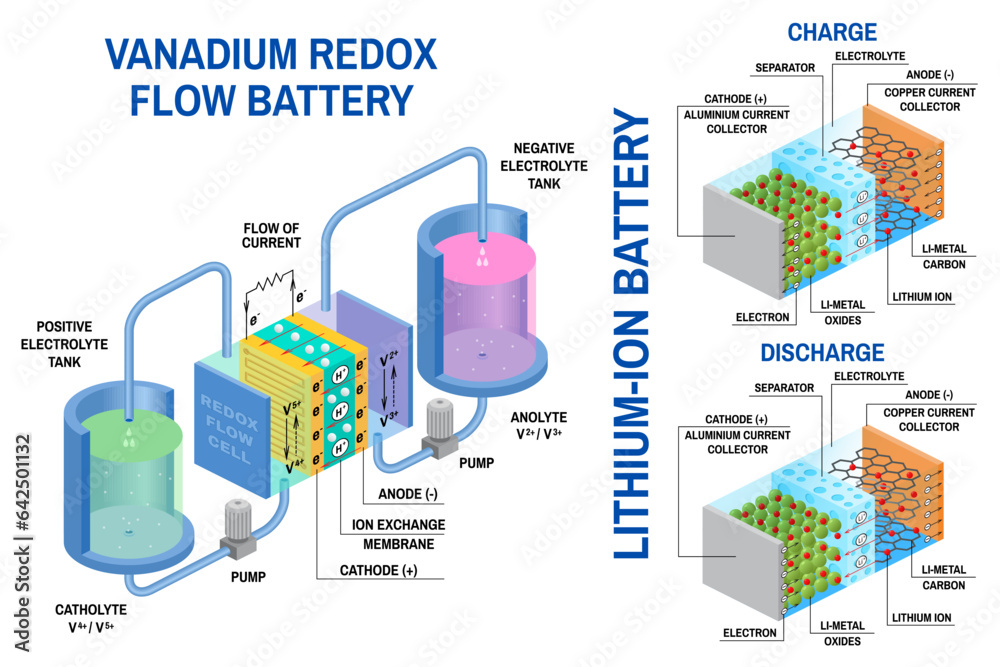
- Anode: The negative electrode, where oxidation occurs. It releases electrons.
- Cathode: The positive electrode, where reduction occurs. It accepts electrons.
- Electrolyte: A solution or paste that conducts ions between the electrodes, facilitating the flow of current.
When a battery is connected to a circuit, a chemical reaction occurs within the electrolyte, causing electrons to flow from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit. This flow of electrons creates an electric current, providing power to the connected device.
The energy stored in a battery is determined by the chemical composition of the electrodes and the electrolyte. The difference in electrical potential between the anode and cathode, known as the electromotive force (EMF), determines the voltage of the battery.
Battery Development
The development of batteries has a long and fascinating history, with significant milestones achieved over centuries.
- 1800: Alessandro Volta invented the first electric battery, known as the voltaic pile. It consisted of alternating discs of zinc and copper separated by cloth soaked in salt water.
- 1836: John Frederic Daniell developed the Daniell cell, a more practical and reliable battery that used copper and zinc electrodes in solutions of copper sulfate and zinc sulfate.
- 1859: Gaston Planté invented the lead-acid battery, which is still widely used today in vehicles. This battery uses lead plates immersed in sulfuric acid solution.
- 1896: Waldemar Jungner developed the nickel-cadmium (NiCd) battery, a rechargeable battery that offered improved performance and durability compared to previous technologies.
- 1959: The first lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery was developed by John B. Goodenough and M. Stanley Whittingham. Li-ion batteries have become the dominant battery technology due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and low weight.
The continuous development of battery technology has led to advancements in battery capacity, energy density, lifespan, and safety, paving the way for a wide range of applications in various industries.
Battery Applications: What Is Battery
Batteries have become an indispensable part of our modern lives, powering a wide range of devices and systems that enhance our daily experiences and drive technological advancements. From the smallest portable electronics to the largest electric vehicles and energy storage systems, batteries play a crucial role in enabling a sustainable and efficient future.
Portable Electronics
The portability and convenience of electronic devices are largely attributed to the widespread use of batteries. These devices, ranging from smartphones and laptops to tablets and wearable fitness trackers, rely on batteries to provide the necessary power for their operation.
The key requirements for batteries in portable electronics include:
- High energy density: To maximize device runtime and minimize the need for frequent charging, batteries in portable electronics must have a high energy density, enabling them to store a significant amount of energy in a compact size.
- Long lifespan: To ensure the longevity of the device, the batteries must have a long lifespan, capable of withstanding numerous charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation in performance.
- Lightweight and compact design: Portable devices are designed to be lightweight and compact, requiring batteries with a small form factor to minimize their overall size and weight.
- Safety: Safety is paramount in portable electronics, and batteries must be designed to prevent overheating, short circuits, and other potential hazards that could compromise user safety.
The development of lithium-ion batteries has revolutionized the portability of electronic devices, enabling longer runtimes, faster charging, and more compact designs.
Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining increasing popularity as a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. Batteries are the heart of EVs, providing the energy needed to power the electric motors that propel the vehicle.
The specific requirements for EV batteries include:
- High energy density: To maximize the driving range of EVs, batteries must have a high energy density, allowing them to store a large amount of energy in a relatively small space.
- Fast charging: To reduce the time spent charging, EV batteries need to be able to charge quickly, minimizing the inconvenience associated with recharging.
- Long lifespan: EV batteries must have a long lifespan to ensure the vehicle remains functional and reliable over its intended service life.
- Robustness and durability: EV batteries are subjected to harsh conditions, including temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and potential impacts, requiring them to be robust and durable to withstand these challenges.
- Cost-effectiveness: The cost of batteries is a significant factor in the overall price of EVs, and cost-effective battery technologies are crucial for making EVs more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Current research and development efforts are focused on improving the energy density, charging speed, and lifespan of EV batteries, while also addressing the challenges of cost and safety.
Energy Storage Systems
Batteries play a vital role in energy storage systems, which are designed to store excess energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind power. By storing energy during periods of high generation and releasing it during periods of high demand, battery storage systems help to stabilize the grid and improve the reliability of renewable energy sources.
The specific requirements for batteries in energy storage systems include:
- High capacity: Energy storage systems require batteries with a high capacity to store significant amounts of energy for extended periods.
- Long lifespan: These systems are expected to operate for many years, requiring batteries with a long lifespan to ensure their long-term performance and reliability.
- Efficiency: Batteries in energy storage systems should have high efficiency, minimizing energy losses during charging and discharging cycles.
- Safety and stability: Energy storage systems are often located in close proximity to residential areas, necessitating batteries that are safe and stable, minimizing the risk of hazards.
The development of advanced battery technologies, such as flow batteries and grid-scale lithium-ion batteries, is expanding the capabilities of energy storage systems, enabling the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
Medical Devices
Batteries are essential components in a wide range of medical devices, from pacemakers and defibrillators to insulin pumps and hearing aids. These devices rely on batteries to provide the power needed for their operation, ensuring the delivery of critical medical care to patients.
The specific requirements for batteries in medical devices include:
- Reliability and safety: Medical devices must operate reliably and safely, requiring batteries that are highly reliable and designed to prevent malfunctions or hazards that could compromise patient health.
- Long lifespan: Medical devices often require long-term use, necessitating batteries with a long lifespan to minimize the need for frequent replacements and ensure uninterrupted device functionality.
- Biocompatibility: Batteries used in implantable medical devices must be biocompatible, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or tissue damage within the body.
- Miniaturization: Many medical devices, such as pacemakers and hearing aids, require small and compact batteries to fit within the device and minimize their impact on the patient’s body.
Research and development in battery technology are continuously improving the performance and safety of batteries used in medical devices, enabling the development of more advanced and life-saving medical treatments.
What is battery – A battery is a device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy. Just like a battery powers our devices, Skai Jackson’s son is a source of energy and inspiration for her, driving her to excel in her career.
The same way we recharge our batteries, we can find motivation and inspiration from those around us, empowering us to reach our full potential.
In the realm of law, “battery” refers to the unlawful application of force to another person. It’s important to remember that everyone is presumed innocent until proven guilty, and recent reports about Skai Jackson in jail should be viewed with that in mind.
The concept of battery underscores the importance of respecting personal boundaries and the legal consequences of violating them.